Standardized generalized hyperbolic Student-t Distribution
dist-sght.RdDensity, distribution function, quantile function and random generation for the standardized generalized hyperbolic Student-t distribution.
Usage
dsght(x, beta = 0.1, delta = 1, mu = 0, nu = 10, log = FALSE)
psght(q, beta = 0.1, delta = 1, mu = 0, nu = 10)
qsght(p, beta = 0.1, delta = 1, mu = 0, nu = 10)
rsght(n, beta = 0.1, delta = 1, mu = 0, nu = 10)Arguments
- x, q
a numeric vector of quantiles.
- p
a numeric vector of probabilities.
- n
number of observations.
- beta
-
numeric value,
betais the skewness parameter in the range(0, alpha). - delta
-
numeric value, the scale parameter, must be zero or positive.
- mu
-
numeric value, the location parameter, by default 0.
- nu
-
a numeric value, the number of degrees of freedom. Note,
alphatakes the limit ofabs(beta), andlambda=-nu/2. - log
a logical, if TRUE, probabilities
pare given aslog(p).
Details
dsght gives the density,
psght gives the distribution function,
qsght gives the quantile function, and
rsght generates random deviates.
These are the parameters in the first parameterization.
Examples
## rsght -
set.seed(1953)
r = rsght(5000, beta = 0.1, delta = 1, mu = 0, nu = 10)
plot(r, type = "l", col = "steelblue",
main = "gh: zeta=1 rho=0.5 lambda=1")
 ## dsght -
# Plot empirical density and compare with true density:
hist(r, n = 50, probability = TRUE, border = "white", col = "steelblue")
x = seq(-5, 5, length = 501)
lines(x, dsght(x, beta = 0.1, delta = 1, mu = 0, nu = 10))
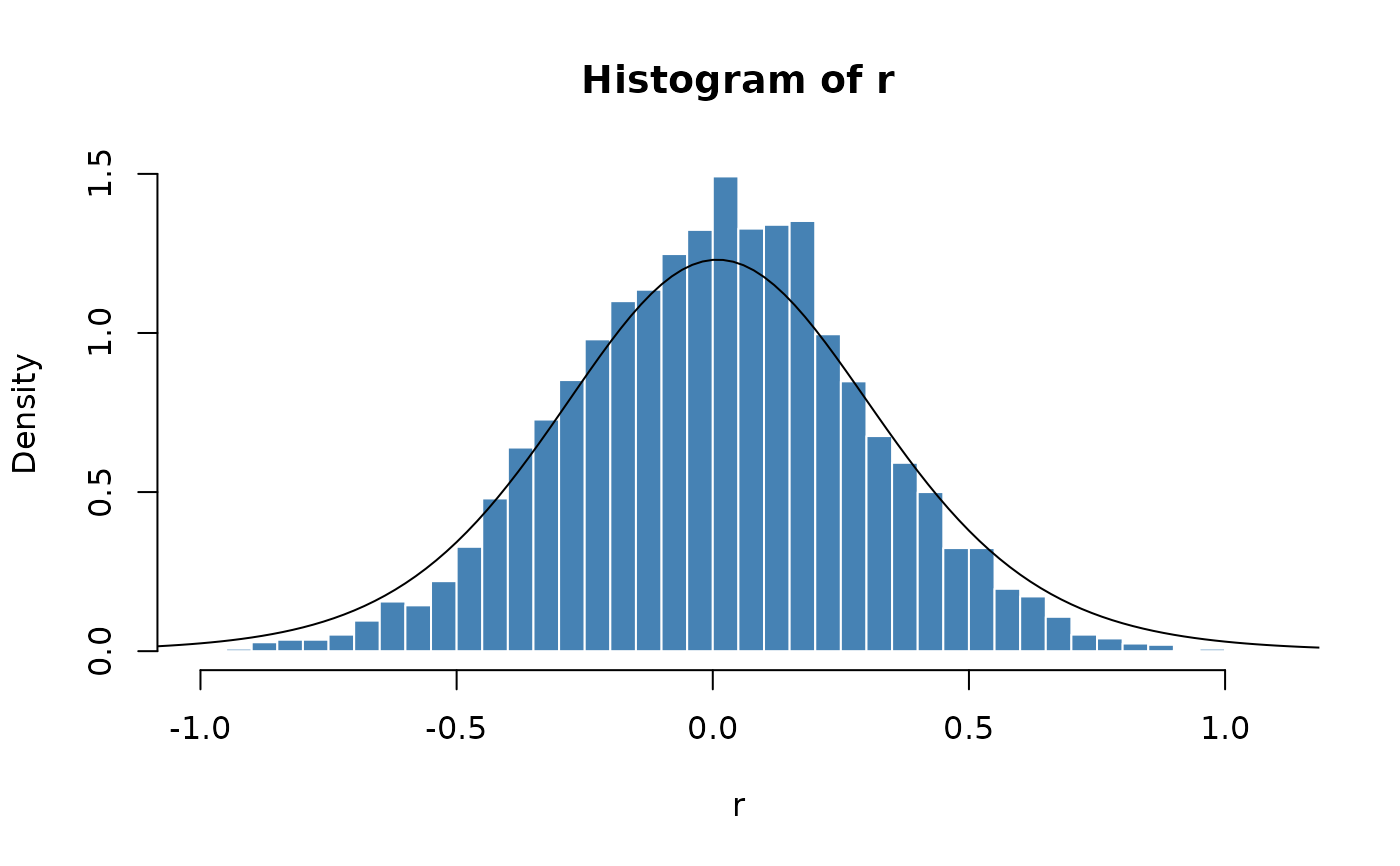
## dsght -
# Plot empirical density and compare with true density:
hist(r, n = 50, probability = TRUE, border = "white", col = "steelblue")
x = seq(-5, 5, length = 501)
lines(x, dsght(x, beta = 0.1, delta = 1, mu = 0, nu = 10))
 ## psght -
# Plot df and compare with true df:
plot(sort(r), (1:5000/5000), main = "Probability", col = "steelblue")
lines(x, psght(x, beta = 0.1, delta = 1, mu = 0, nu = 10))
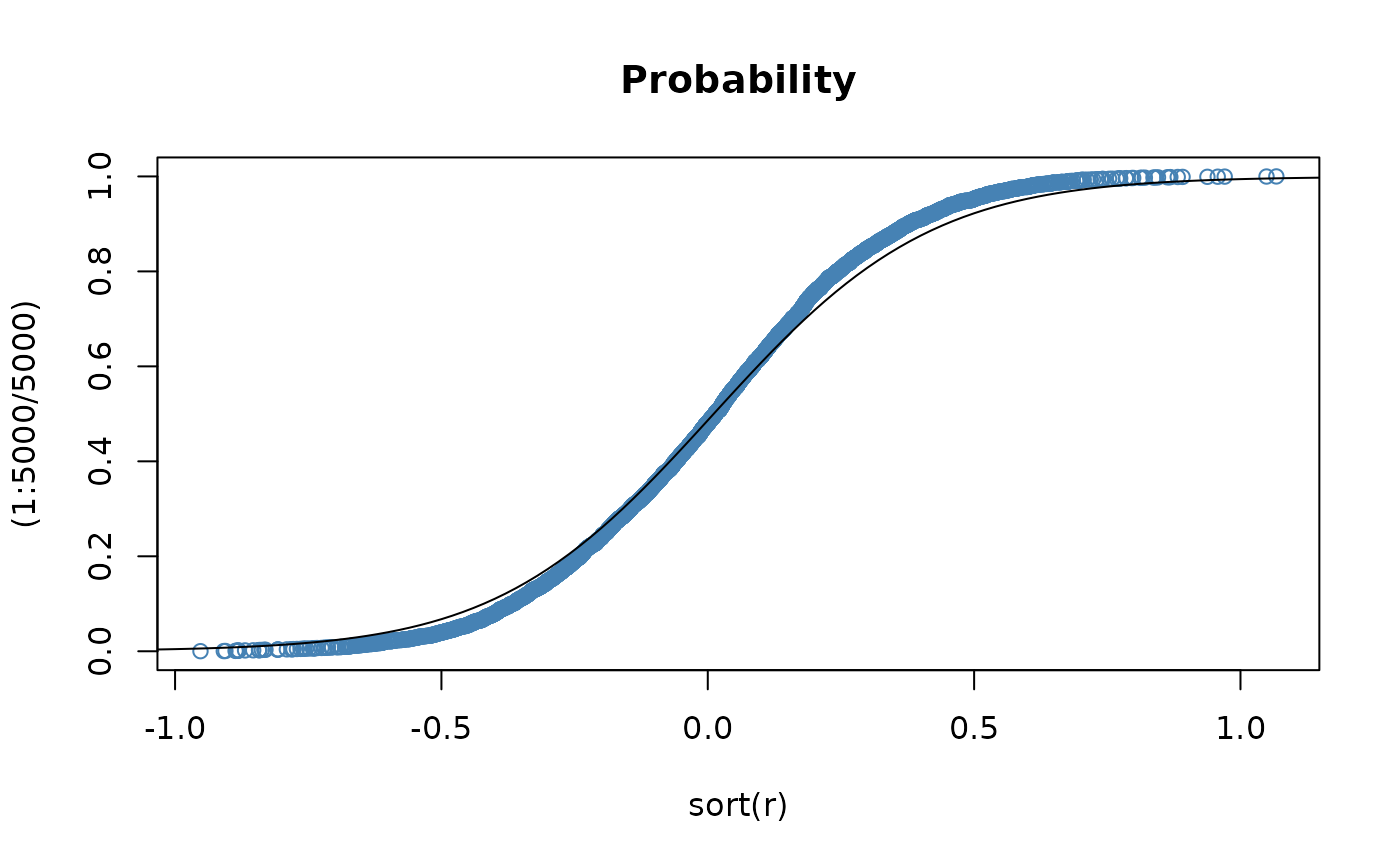
## psght -
# Plot df and compare with true df:
plot(sort(r), (1:5000/5000), main = "Probability", col = "steelblue")
lines(x, psght(x, beta = 0.1, delta = 1, mu = 0, nu = 10))
 ## qsght -
# Compute Quantiles:
round(qsght(psght(seq(-5, 5, 1), beta = 0.1, delta = 1, mu = 0, nu =10),
beta = 0.1, delta = 1, mu = 0, nu = 10), 4)
#> [1] -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5
## qsght -
# Compute Quantiles:
round(qsght(psght(seq(-5, 5, 1), beta = 0.1, delta = 1, mu = 0, nu =10),
beta = 0.1, delta = 1, mu = 0, nu = 10), 4)
#> [1] -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5